Security
When you deploy a GraphQL schema, Dgraph automatically generates the query and mutation operations for each type and exposes them as a GraphQL API on the /graphql endpoint.
Dgraph’s GraphQL authorization features let you specify :
- if the client requires an API key or notif anonymous access is allowed to invoke a specific operation of the API.
- if a client must present an identity in the form of a JWT token to use the API.
- RBAC rules (Role Based Access Control) at operation level based on the claims included in the client JWT token.
- ABAC rules (Attribute Based Access COntrol) at data level using graph traversal queries.
/graphql endpoint.
Refer to the following documentation to set your /graphql endpoint security :
/graphql security flow
In summary, the Dgraph security flow on /graphql endpoint is as follow:
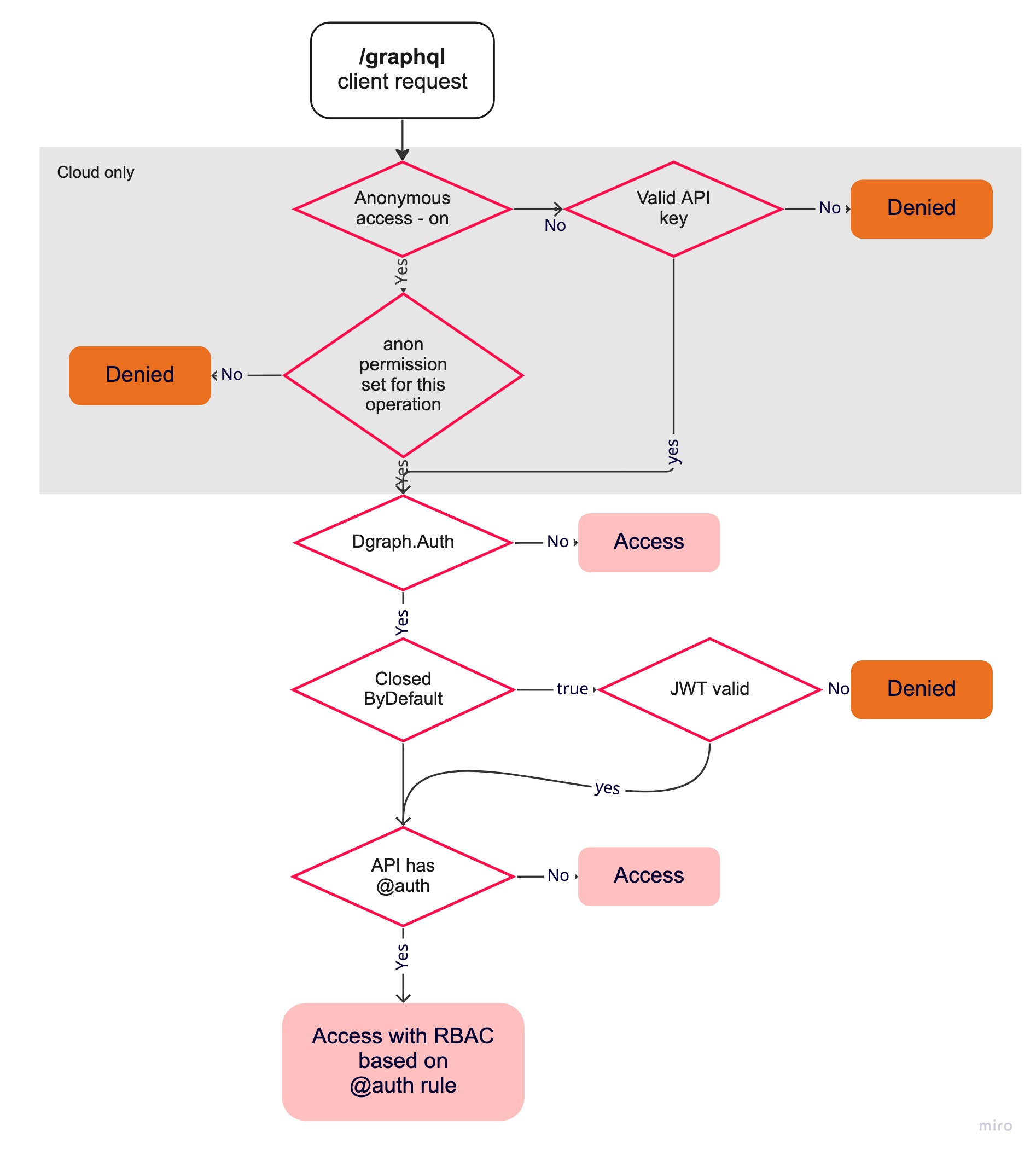
graphql endpoint security
CORS
Additionally, you can restrict the origins that /graphql endpoint responds to.
This is a best practice to prevent XSS exploits.
Authentication
Dgraph’s GraphQL authorization relies on the presence of a valid JWT token in the request.
Dgraph supports both symmetric (HS256) and asymmetric (RS256) encryption and accepts JSON Web Key (JWK) URL or signed JSON Web Token (JWT).
You can use any authentication method that is capable of generating such JWT token (Auth0, Cognito, Firebase, etc…) including Dgraph login mechanism.
ACL
Note that another token may be needed to access the system if ACL security is also enabled. See the ACLs section for details. The ACLs are a separate security mechanism.
JWT Claims
In JSON web tokens (JWTs) (https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc7519) , a claim appears as a name/value pair.
When we talk about a claim in the context of a JWT, we are referring to the name (or key). For example, the following JSON object contains three claims sub, name and admin:
{
"sub": "1234567890",
"name": "John Doe",
"admin": true
}
So that different organizations can specify different claims without conflicting, claims typically have a namespace, and it’s a good practice to specify the namespace of your claims. put specific claims in a nested structure called a namespace.
{
"https://mycompany.org/jwt/claims": {
"username": "auth0|63fe77f32cef38f4fa3dab34",
"role": "Admin"
},
"name": "raph@dgraph.io",
"email": "raph@dgraph.io",
"email_verified": false,
"iss": "https://dev-5q3n8cc7nckhu5w8.us.auth0.com/",
"aud": "aqk1CSVtliyoXUfLaaLKSKUtkaIel6Vd",
"iat": 1677705681,
"exp": 1677741681
}
This json is a JWT token payload containing a namespace https://mycompany.org/jwt/claims having a username claim and a role claim.